Evidence of Turmeric's Benefit against Systemic Fungal Infection
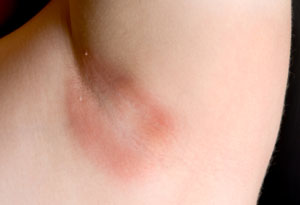

Lab and animal research suggest that turmeric and its compounds can help prevent and treat systemic fungal infections. Turmeric's antifungal properties have even been put to use in soaps to help heal skin wounds in patients infected with HIV. In a turmeric-based antibacterial soap, the herb inhibited Candida albicans and bacteria. (v.22, 25, 99)
Turmeric's Essential Oils
Studies show that the essential oils from turmeric's leaf and rhizome have antifungal activity against multiple fungal species that can cause systemic infections. These include: (v.118)
- Various Candida species.
- Cryptococcus neoformans.
- Sporothrix schenckii.
Turmeric oil also exerts strong antibacterial and antimicrobial effects. These can be helpful with concurrent bacterial infections. Oil from turmeric leaves appears to work better than oil from its rhizome. (v.27, 106)
Prevents Production of Carcinogenic Aflatoxins
Aflatoxins are cancer-causing substances produced by certain fungi. Lab studies show turmeric leaf oil effectively stops over 95% of growth of Aspergilli fungi. Depending on the concentration used, turmeric leaf oil also suppressed 95-100% of aflatoxin production by Aspergillus flavus. (v.107)
In particular, turmeric oil blocks mycotoxin genes. It also disrupts fungal cell membranes and functions. Animal studies confirm that turmeric's essential oil may prevent the toxic effects of aflatoxins. (v.243)
The main compounds in turmeric leaf oil include: (v.107)
Other turmeric leaf compounds include: (v.107)
Dried turmeric rhizome powder prevents DNA mutations in liver cells. This may help prevent the development of liver cancer. (v.107, 123-124)
Whole turmeric rhizome extracts mostly contain ar-turmerone. Lab tests show turmeric rhizome extracts inhibit A. flavus. They also block over 90% of aflatoxin production by A. parasiticus. Conversely, using the turmeric compound curcumin by itself doesn't appear to block any aflatoxins from this Aspergilli fungus. (v.5, 107)
Individual Turmeric Compounds with Antifungal Effects
Many of the micronutrients and polyphenols in turmeric individually have potent antioxidant, fungicidal, and/or immune-boosting effects as well. These include:
| TURMERIC COMPOUND and FUNGUS | EFFECT |
|---|---|
|
CURCUMIN combined with LED light (lab tests) Candida albicans, C. glabrata, and C. tropicalis |
|
|
CURCUMIN with piperine (animal study) Candida albicans |
|
|
CURCUMIN (lab studies) Candida albicans, C. dubliniensis, C. glabrata, C. krusei, and C. tropicalis |
|
|
CURCUMIN (lab studies) Paracoccidioides brasiliensis |
|
|
CURCUMIN (lab studies) Cryptococcus neoformans |
|
|
CURCUMIN (lab studies) Sporothrix schenckii |
|
|
(lab studies) Candida albicans, C. glabrata, C. kruzei, and C. tropicalis |
|
|
(lab studies) Candida albicans and dermatophytes |
|
|
α-TERPINEOL (v.73, 75) (lab studies) Candida albicans, C. glabrata |
|
|
(lab studies) Candida albicans |
|
|
(lab studies) Candida albicans |
|
|
(lab studies) Candida albicans |
|
|
(lab studies) Candida albicans, C. glabrata, C. kruzei, C. lusitaniae, C. parapsilosis, and C. tropicalis; Cryptococcus neoformans |
|
|
(lab studies) Candida albicans and Aspergillus niger |
|
|
(lab studies) Candida albicans and C. parapsilosis |
|
|
(lab studies) Candida albicans, Cryptococcus neoformans, Sporothrix schenckii |
|
|
γ-TERPINENE (v.73, 75) (lab studies) Candida albicans, C. glabrata |
|
|
(lab studies) Candida albicans, Cryptococcus neoformans |
|
|
(lab studies) Candida albicans, C. tropicalis, C. glabrata, C. kruzei; dermatophytes |
|
|
(lab studies) Candida |
|
Join the 1000s of People Who Are Discovering the Benefits of Turmeric.

Healthceuticals® Turmeric Curcumin Complex
100% Certified
Organic ingredients
- Organic Turmeric Extract - standardized to 95% curcuminoids.
- Organic Whole Turmeric - provides full spectrum antioxidant, anti-inflammatory turmeric benefits, including turmerones and numerous vitamins, minerals, and phytonutrients
- Organic Black Pepper Extract - standardized to 95% piperine; dramatically enhances bioavailablity.
- Organic Phospholipids - markedly improve absorption.
- Organic Ginger - works synergistically with turmeric to provide more powerful benefits.
- Absolutely FREE of potentially harmful additives and fillers such as magnesium stearate.




