What Causes Parkinson's Disease?

Accumulation of damage from free radicals and inflammation are both part of a self-feeding degenerative cycle of events. In the brain, this cycle can lead to destruction of the brain cells that produce dopamine. This important neurotransmitter sends signals in and from the brain to control muscle movement. (iv.3, 8, 31-32)
The brain is especially prone to damage from free radicals because of the following factors: (iv.3, 8, 31-32)
- It's composed of high levels of lipids (fats), which are easily oxidized by free radicals.
- Brain functions use lots of oxygen — which creates free radicals.
- Low levels of natural antioxidants make it difficult to offset abnormally high levels of free radicals.
For example, brain's metabolism of dopamine itself generates free radicals. Under normal healthy conditions, this is balanced by the production of natural antioxidants. (iv.32)
Chronic Inflammatory Conditions Increase the Risk of Parkinson's Disease
Psychological and social stress, nutritional deficiencies, a dysfunctional immune system, and leaky gut can lead to and worsen chronic inflammatory diseases. These include diseases such as diabetes, cancer, and chronic low-level infection. All of these conditions overwhelm the nutritional and antioxidant resources in the body. The situation worsens over time as the body is increasingly unable to maintain a healthy biochemical balance: (iv.28, 39, 60, 69, 101)
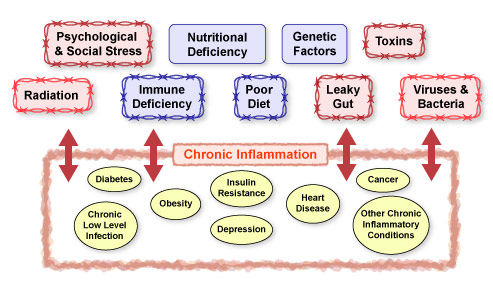
Figure IV.15: Factors that Contribute to Chronic Inflammatory Conditions
Damage to Mitochondria in Brain Cells
NITRIC OXIDE (NO) & THE BRAIN
Nitric oxide (NO) is a highly reactive free radical. It's produced in the body by enzymes called nitric oxide synthases (NOS or iNOS). Under normal conditions, NO behaves as a neurotransmitter and antimicrobial substance. (iv.102)
When the brain is in a chronic inflammatory state, overstimulated astrocyte immune system cells release lots of NOS. The high levels of NO they produce are extremely toxic to neurons. Studies show that curcumin can suppress abnormal levels of NOS and NO free radicals. (iv.102)
In the brain, inflammation also stimulates receptors on brain cells that release glutamate. Under normal conditions, glutamate is an important neurotransmitter chemical in the brain. It stimulates, or excites, neuron brain cells to send and receive signals necessary for brain activity. (iv.1, 8, 30-33, 39, 102-103)
But chronic inflammation continuously stimulates these receptors. This creates hypersensitive, overexcited brain cells that keep glutamate levels abnormally high and reduce antioxidant levels. A toxic loop develops - overstimulated immune system cells, inflammatory proteins, and overexcited brain cells inhibiting natural antioxidants and promoting free radicals that cause oxidative damage and more inflammation: (iv.1, 8, 30-33, 39, 102-103)
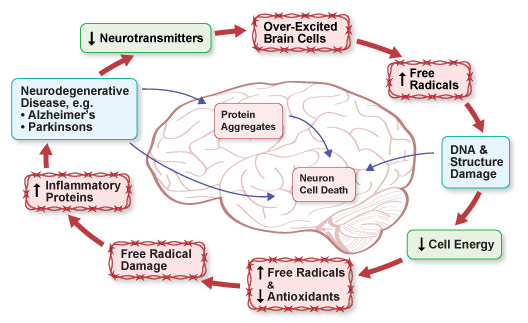
Figure IV.16: Inflammation and Brain Cell Death in Parkinson's Disease
Damage to the cell's DNA and mitochondria are also part of this disastrous cascade effect in Parkinson's disease. They result in impaired enzyme and protein activity, which causes: (iv.1, 8, 30-33, 39, 102-103)
- Decreased production of cell energy.
- Inability to clear the free radicals naturally produced when glucose is metabolized by cells to make cell energy.
- Disabled mitophagy — the internal maintenance system that gets rid of damaged, pro-inflammatory mitochondria.
- Failure to encapsulate the neurotransmitter dopamine — when dopamine is left exposed it is easily oxidized and produces more free radicals and inflammation.
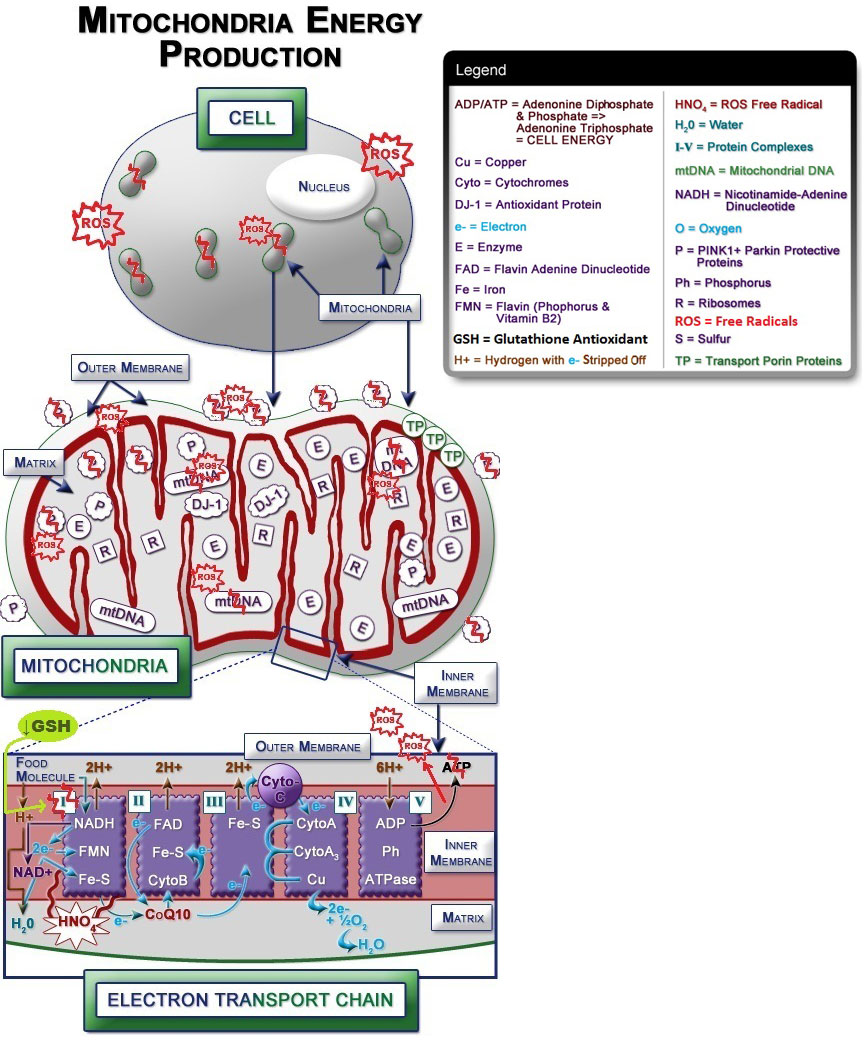
Figure IV.17: Damaged & Dysfunctional Mitochondria Contribute to Parkinson's Disease
Eventually this leads to clumps of proteins that form lesions called Lewy bodies. These lesions destroy neuron brain cells responsible for producing the neurotransmitter dopamine, causing the symptoms of Parkinson's disease. (iv.8, 30-33, 103)
Join the 1000s of People Who Are Discovering the Benefits of Turmeric.

Healthceuticals® Turmeric Curcumin Complex
100% Certified
Organic ingredients
- Organic Turmeric Extract - standardized to 95% curcuminoids.
- Organic Whole Turmeric - provides full spectrum antioxidant, anti-inflammatory turmeric benefits, including turmerones and numerous vitamins, minerals, and phytonutrients
- Organic Black Pepper Extract - standardized to 95% piperine; dramatically enhances bioavailablity.
- Organic Phospholipids - markedly improve absorption.
- Organic Ginger - works synergistically with turmeric to provide more powerful benefits.
- Absolutely FREE of potentially harmful additives and fillers such as magnesium stearate.




